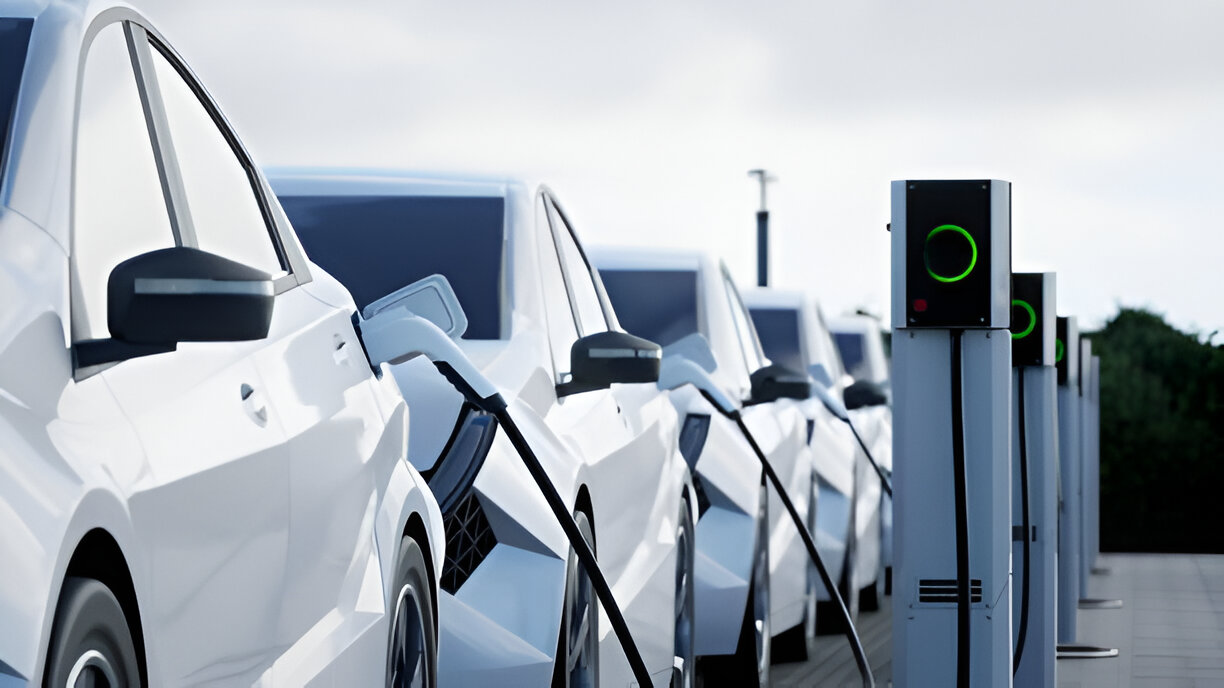
Budget Charging: Home and Public EV Charging Costs Explained
As electric vehicles (EVs) continue to gain popularity, understanding the costs associated with charging them becomes increasingly important. Whether you’re already an EV owner or considering making the switch, knowing how to charge on a budget can significantly impact your overall savings. In this blog post, we’ll break down the costs of home and public EV charging, helping you make informed financial decisions.
Home Charging Costs
Home charging is often the most convenient and cost-effective way to keep your EV powered. Here’s what you need to consider:
- Initial Setup Costs:
- Level 1 Chargers: These come with your vehicle and plug into a standard 120V outlet. While they have no additional setup cost, charging times are much longer.
- Level 2 Chargers: For faster charging, many opt for a Level 2 charger, which requires a 240V outlet. Installation can range from $500 to $2,000 depending on your electrical system.
- Electricity Rates:
- Electricity rates vary significantly depending on your location and provider. On average, residential rates in the U.S. are about $0.13 per kWh.
- Consider off-peak rates. Many utility companies offer lower rates during off-peak hours, usually at night, which can reduce your costs if you charge your EV during these times.
- Maintenance Costs:
- Home chargers are generally low maintenance, but it’s wise to account for potential future repairs or upgrades.
Public Charging Costs
Public charging stations can be found in various locations, from shopping centers to dedicated charging hubs. Here’s what you need to know:
- Types of Chargers:
- Level 2 Public Chargers: These are more common and generally less expensive than DC fast chargers but still offer quicker charging than Level 1 home chargers.
- DC Fast Chargers: These charge your EV much faster but often come at a higher cost. They are ideal for long trips when you need a quick top-up.
- Pricing Models:
- Pay-Per-Use: Many stations charge per kWh, with prices ranging from $0.20 to $0.60 per kWh. Some charge by time, such as per minute or hour.
- Subscription Services: Some networks offer monthly plans that provide discounted rates or unlimited charging for a fixed fee. This can be beneficial if you frequently use public chargers.
- Membership Fees:
- Joining a charging network can offer benefits like reduced rates and access to more charging locations, but be sure to calculate whether the membership fee outweighs the pay-per-use costs for your typical usage.
Tips for Charging on a Budget
- Plan Your Charging Schedule: Utilize home charging during off-peak hours to save on electricity costs.
- Take Advantage of Incentives: Check for any available government rebates or incentives for installing a home charger.
- Compare Public Charging Options: Use apps or websites to find the most cost-effective charging stations near you.
- Optimize Charging: Charge your vehicle to 80% rather than 100% to prolong battery life and reduce time spent at public stations.
By understanding the costs associated with both home and public charging, you can make smarter choices that keep your budget in check while enjoying the benefits of driving an electric vehicle. As the EV market continues to evolve, staying informed will help you maximize savings and efficiency.
Add a comment Cancel reply
Categories
- Car News (10)
- Car Reviews (7)
- Educational Tips (7)
- Electric Cars (9)
- EV Battery (1)
- EV Charging (8)
- EV Testing (3)
- Uncategorized (28)
Recent Posts
Related posts


EV Charging Infrastructure in Canada: Current Maps and Expansion Plans

Top Portable EV Chargers